Published: Jan 29, 2024 by FME Lab
Halophilic and halotolerant bacteria are generally considered to live in natural environments such as see, although they can also be present in foods such as cheese and seafood. These salt-loving bacteria have occasionally been characterized in cheeses, and studies on their ecological and technological functions are still rare. In a previous study, we systematically characterized these micro-organisms in the rind of 13 traditional cheeses. We identified 35 halotolerant strains1, 8 of which were assigned to the Halomonas genus on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis.
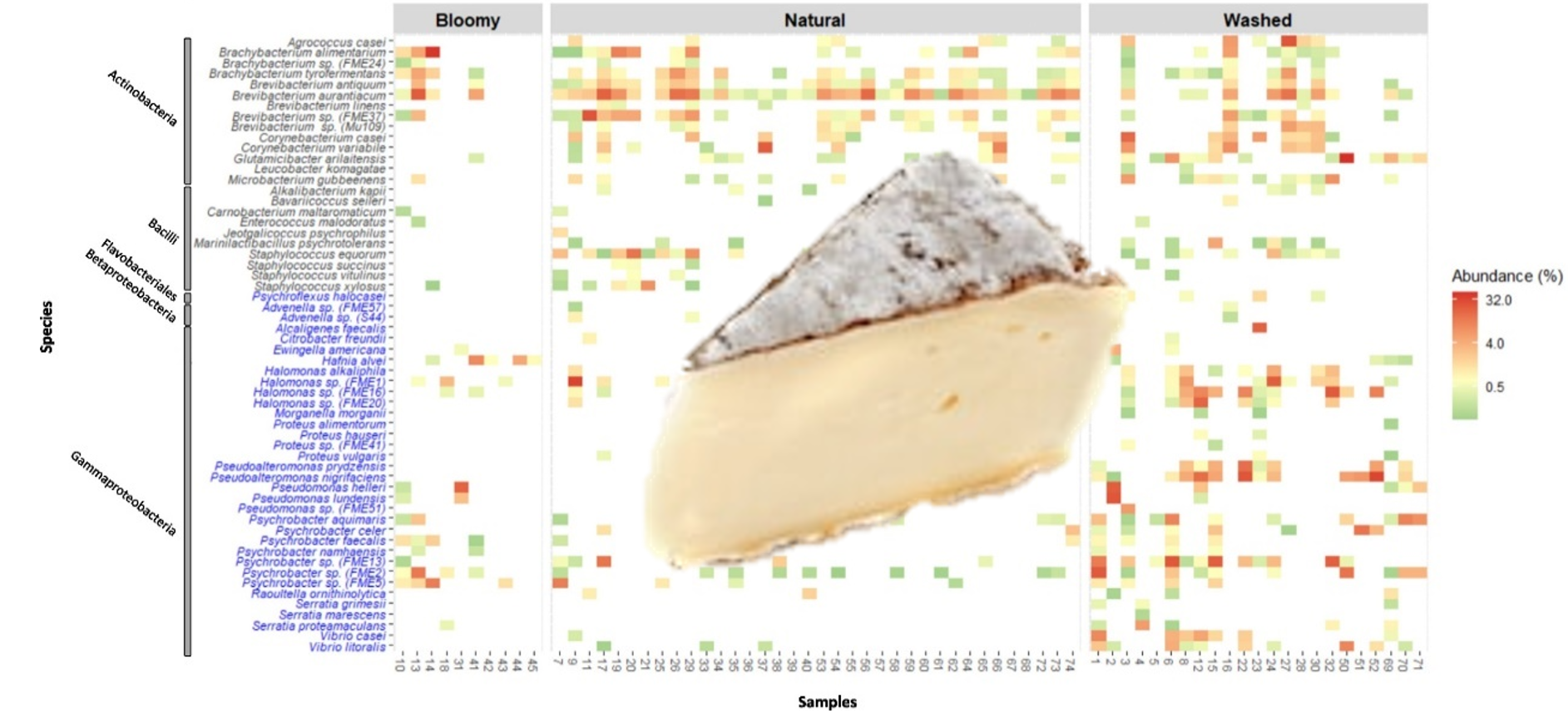
A combination of phylogenetic and genomic analyses revealed that they constituted three new, well-supported groups. Further phenotypic, phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic analyses allowed us to classify these isolates as three new Halomonas species, to which the names Halomonas citrativorans sp. nov, Halomonas casei sp. nov and Halomonas colorata sp. nov were assigned. These species appear to be frequent and abundant in several types of cheese, indicating that they may play a role in their manufacture and quality. Cheeses still offer researchers something to sink their teeth into !
-
Kothe et al. Halomonas citrativorans sp. nov., Halomonas casei sp. nov. and Halomonas colorata sp. nov., isolated from French cheese rinds. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024 ↩


